The Biomaker Africa programme is an initiative by the Open Plant fund, Synthetic Biology Strategic Research Initiative (Synbio SRI) and University of Cambridge. The programme been the first of its kind in Africa is aimed at training biologists and non-biologists through the “Biomaker Training” programme to Learn, Design, Prototype and Share science hardware designs critical to building tools for laboratory use and for environmental sensing. On the other hand, the Biomaking Africa Programme is geared towards enabling teams design and build solutions to problems in Agriculture, Health, Research and Education peculiar to Africa. The Biomaker Africa Programme is made up of 5 countries namely, Ghana (Kumasi Hive), South Africa (University of Pretoria), Egypt (Mansoura University) and Ethiopia (Bahir Dar University).
-

-

-

-
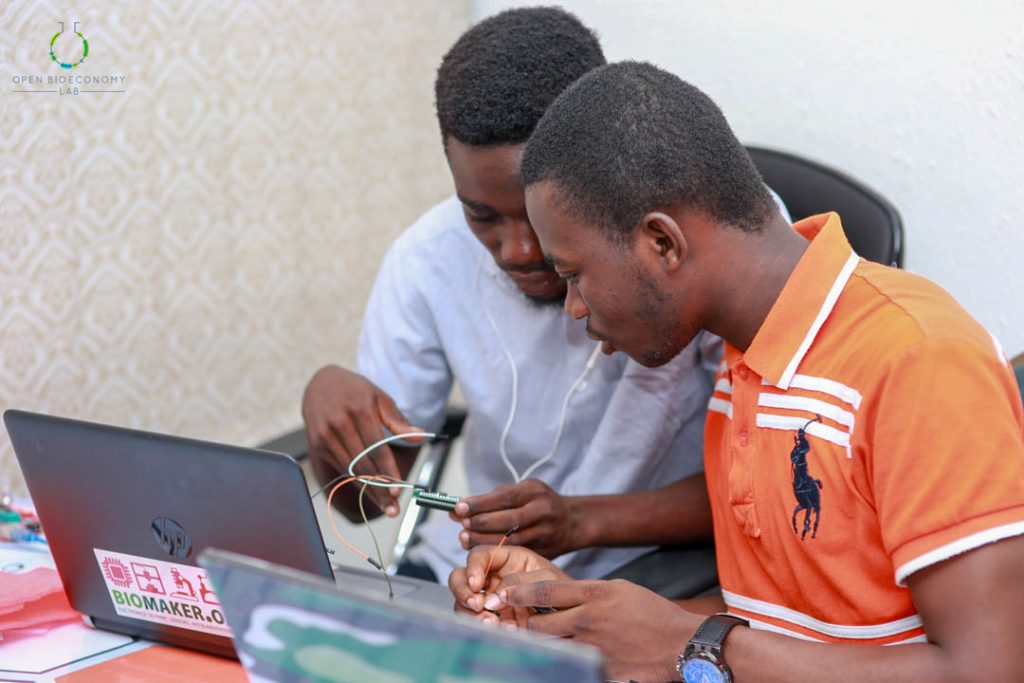

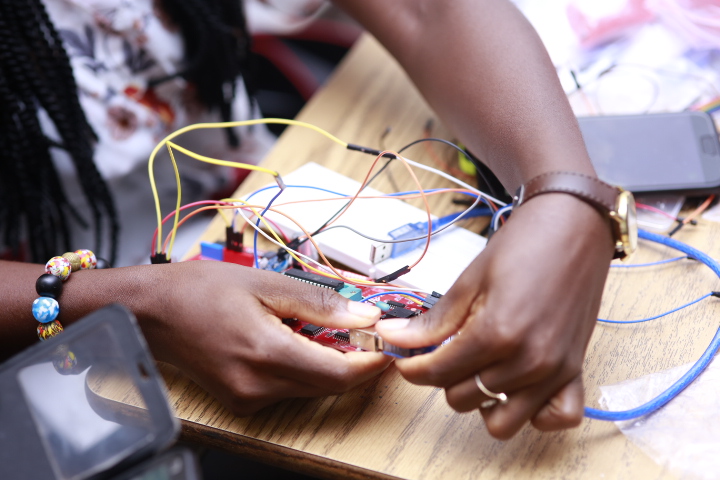
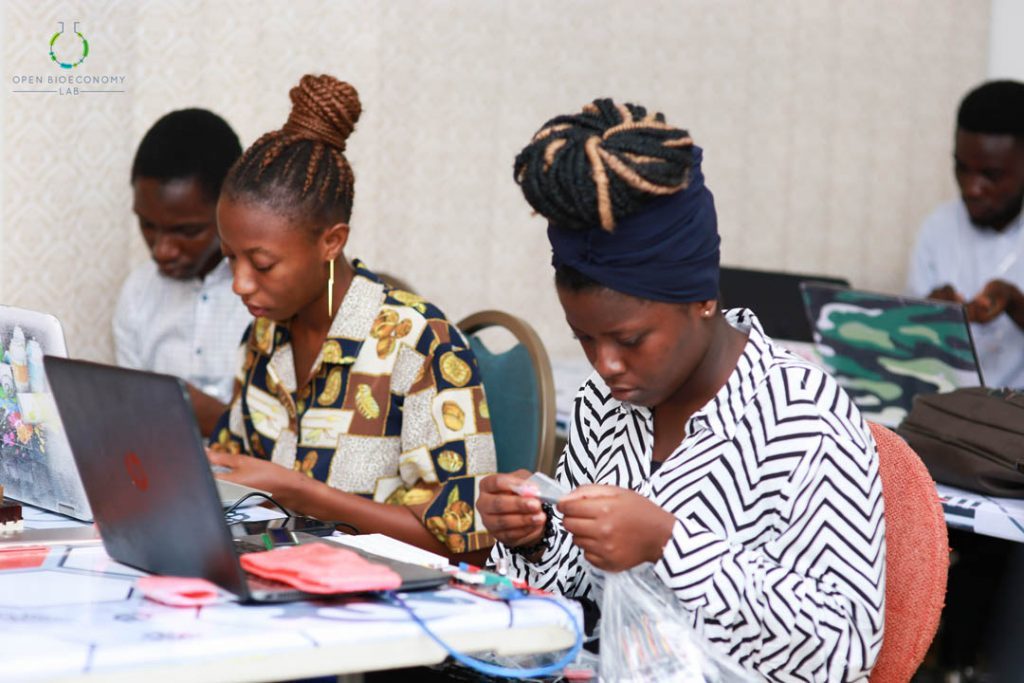
Participants tinkering with XOD and the Open Smart Rich UNO 3 microcontroller
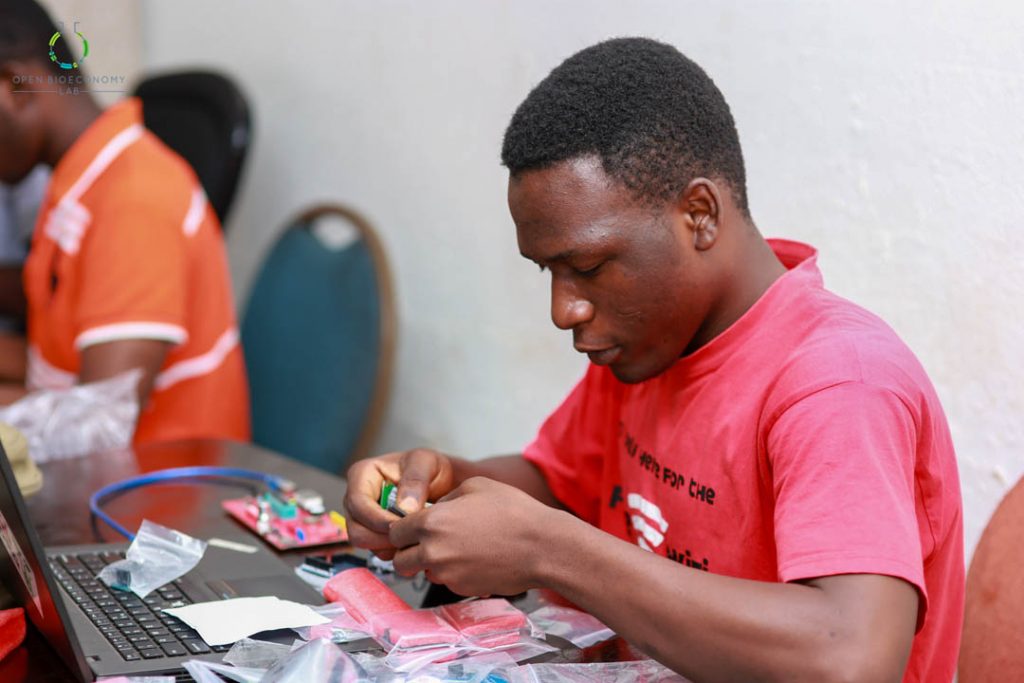
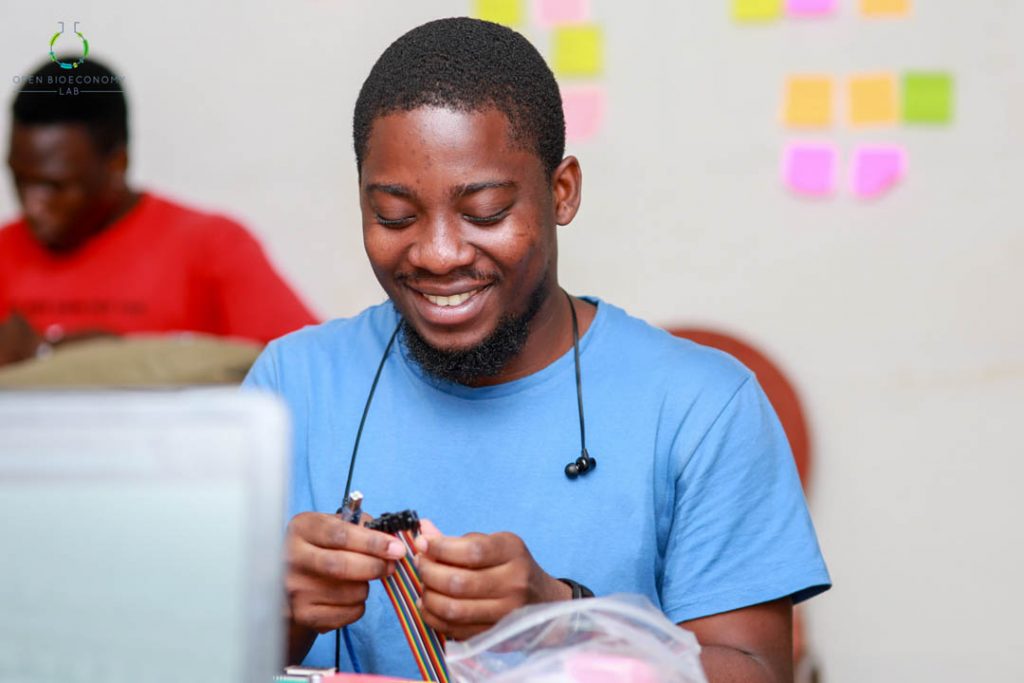
Kumasi Hive, one of the implementing nodes on the Biomaker Africa programme designed a two-months intensive training programme for students and graduates with background in biology and engineering. The training in Kumasi Hive selected 10 participants who were engaged for two months beginning March 2, 2019 to April 13, 2019. The curriculum driving the training was divided into three sections including;
- Introduction to fundamentals of biology
- Introduction to electronics and programming with XOD
- Introduction to 3D printing and laser cutting
- Design thinking the curriculum was designed with the goal of equipping participants with trans-disciplinary knowledge and skills in biology, electronics, programming, 3D printing and design thinking respectively. This we believe will enable the selected participants to build biology solutions to real world challenges peculiar to the Ghanaian context.
Each training track lasted for two weeks and happened only on Saturday and Sunday for two months. The training sessions were characterized by short presentations by trainers, brainstorming sessions and research presentations by the participants. The training ended with a Biomaker hackathon where the participants were provided with the Biomaker kits to build working prototypes in a day. After a design thinking session to expose the 10 participants to the design thinking process and human centered design approach, the participants came out with projects such as;
- A solar powered power pack for gel electrophoresis to be used for field research and indoor laboratory use.
- Colorimeter for urine analysis
- Water quality sensor for testing mercury and lead levels in water samples in mining areas in Ghana.
- Air quality sensor for environmental monitoring.
- Smart DIY biological safety cabinet for BSL1 work.
Some references and testimonies of the participants can be found here at https://www.twitter.com/openbioeconomy