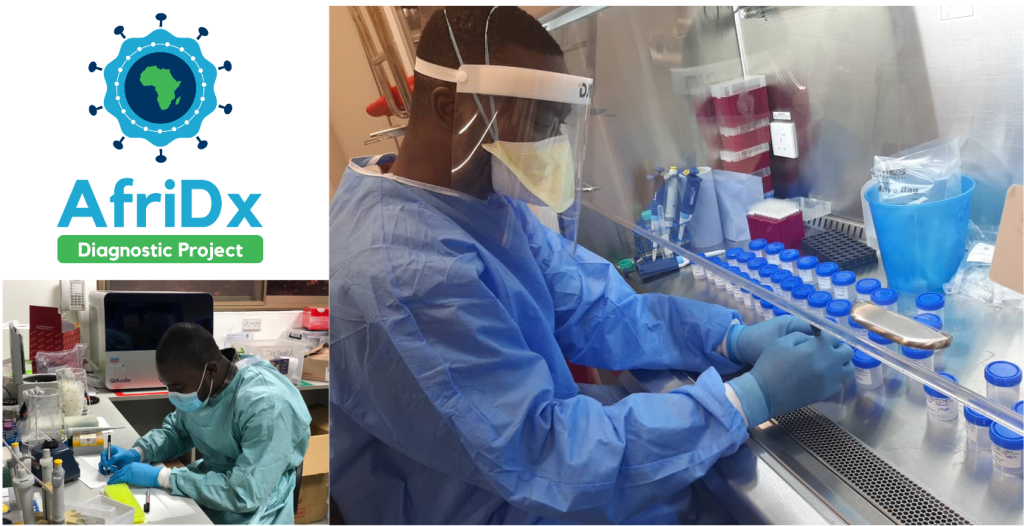
The AfriDx Initiative has officially begun and we’re excited to see what we can achieve.
AfriDx is a 15-month project led by the University of Cambridge with Danish Technical University (DTU), Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research (NMIMR), Kumasi Centre for Collaborative Research in Tropical Medicine (KCCR) and Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology (KNUST).
NMIMR, KCCR are supporting the frontline of SARS-Cov-2 testing in Ghana using RT-qPCR. Their capacity is ~1500 tests/day and they seek a faster lower cost solution without compromise in accuracy or precision. RT-qPCR is slow, and the costs (typically >$10/test) are not sustainable for long term testing. Point of care (POC) diagnostics are only achieved in Africa with significant external grant-aid support. The average annual expenditure on health in low-income countries is <$40 per capita. Local production capabilities are therefore a vital component of any solution as exemplified in May 2019 when WHO, UNIDO, UNCTAD, UNAIDS, UNICEF and The Global Fund released a joint statement promoting local production of medicines and health technologies.
AfriDx will focus on developing a diagnostic system that can be manufactured in country. Additionally, a production process for the required biological materials will be developed to allow for production in Ghana at low cost. Lastly, these systems will allow for the training of skilled and minimally skilled personnel to understand and perform the testing.
We will undertake the following activities:
- Conduct a trial of a prototype POC LAMP (PATHPOD) for detection of viral RNA (SARS-Cov-2) in the COVID testing laboratories in Ghana
- Develop a production process for local manufacture in Ghana of the required biological materials at low cost and produce a version of PATHPOD in Africa for Africa (the AfriDx)
- Screen and isolate scFv’s for a serology antibody titre test, to produce an immun oassay (AfriMx) for late stage infection and post infection immunity
- Train skilled and minimally skilled personnel to understand and perform testing
- Connect with local enterprise in Ghana and develop a plan for exploitation and the route tomarket for the low cost AfriDX and AfriMx diagnostics.
This project will co-develop technology, tools and training which will strengthen Ghana’s capacity to manage outbreaks, both directly and through improved in country manufacturing capability for healthcare diagnostics. In the long-term, greater independence from external grant aid to supply diagnostics and development of a local manufacturing infrastructure is intended to emerge.